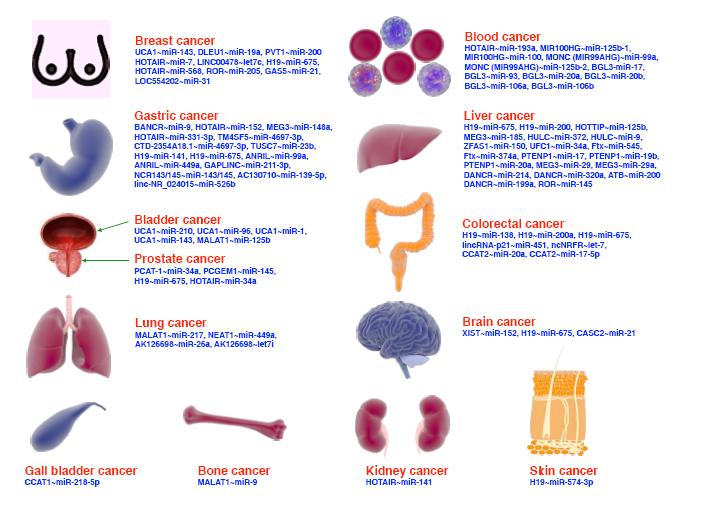
引用本文: 秦環(huán)龍,梁勇. 腸道微生態(tài)變化及臨床應(yīng)用. 中國(guó)普外基礎(chǔ)與臨床雜志, 2011, 18(12): 1237-1241. doi: 復(fù)制
版權(quán)信息: ?四川大學(xué)華西醫(yī)院華西期刊社《中國(guó)普外基礎(chǔ)與臨床雜志》版權(quán)所有,未經(jīng)授權(quán)不得轉(zhuǎn)載、改編
| 1. | Sartor RB. Microbial influences in inflammatory bowel diseases [J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134(2): 577594. |
| 2. | Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, et al. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity [J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7122): 10221023. |
| 3. | O’Hara AM, Shanahan F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ [J]. EMBO Rep, 2006, 7(7): 688693. |
| 4. | Cani PD, Delzenne NM. The gut microbiome as therapeutic target [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 130(2): 202212. |
| 5. | Palmer C, Bik EM, DiGiulio, et al. Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota [J]. PLoS Biol, 2007, 5(7): e177. |
| 6. | Agans R, Rigsbee L, Kenche H, et al. Distal gut microbiota of adolescent children is different from that of adults [J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2011, 77(2): 404412. |
| 7. | Lyra A, Rinttil T, Nikkil J, et al. Diarrhoeapredominant irritable bowel syndrome distinguishable by 16S rRNA gene phylotype quantification [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15(47): 59365945. |
| 8. | Malinen E, Rinttil T, Kajander K, et al. Analysis of the fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients and healthy controls with realtime PCR [J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2005, 100(2): 373382. |
| 9. | Schoepfer AM, Schaffer T, SeiboldSchmid B, et al. Antibodies to flagellin indicate reactivity to bacterial antigens in IBS patients [J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2008, 20(10): 11101118. |
| 10. | Seksik P, RigottierGois L, Gramet G, et al. Alterations of the dominant faecal bacterial groups in patients with Crohn’s disease of the colon [J]. Gut, 2003, 52(2): 237242. |
| 11. | Turner JR. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application [J]. Am J Pathol, 2006, 169(6): 19011909. |
| 12. | Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Glasser AL, et al. CEACAM6 acts as a receptor for adherentinvasive E.coli, supporting ileal mucosa colonization in Crohn disease [J]. J Clin Invest, 2007, 117(6): 15661574. |
| 13. | de Giorgio R, Blandizzi C. Targeting enteric neuroplasticity: diet and bugs as new key factors [J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 138(5): 16631666. |
| 14. | Nalini N, Manju V, Menon VP. Effect of coconut cake on the bacterial enzyme activity in 1,2dimethyl hydrazine induced colon cancer [J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2004, 342(12): 203210. |
| 15. | Iwashita J, Sato Y, Sugaya H, et al. mRNA of MUC2 is stimulated by IL4, IL13 or TNFα through a mitogenactivated protein kinase pathway in human colon cancer cells [J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2003, 81(4): 275282. |
| 16. | Shimizu K, Ogura H, Asahara T, et al. Gastrointestinal dysmotility is associated with altered gut flora and septic mortality in patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome: a preliminary study [J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2011, 23(4): 330335, e157. |
| 17. | Reddy BS, Gatt M, Sowdi R, et al. Surgical manipulation of the large intestine increases bacterial translocation in patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery [J]. Colorectal Dis, 2006, 8(7): 596600. |
| 18. | Li JV, Ashrafian H, Bueter M, et al. Metabolic surgery profoundly influences gut microbialhost metabolic crosstalk [J]. Gut, 2011, 60(9): 12141223. |
| 19. | Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins [J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7228): 480484. |
| 20. | Limdi JK, O’Neill C, McLaughlin J. Do probiotics have a therapeutic role in gastroenterology? [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2006, 12(34): 54475457. |
| 21. | Preidis GA, Versalovic J. Targeting the human microbiome with antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics: gastroenterology enters the metagenomics era [J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 136(6): 20152031. |
| 22. | Moayyedi P, Ford AC, Talley NJ, et al. The efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review [J]. Gut, 2010, 59(3): 325332. |
| 23. | Hun L. Bacillus coagulans significantly improved abdominal pain and bloating in patients with IBS [J]. Postgrad Med, 2009, 121(2): 119124. |
| 24. | Barrett JS, Canale KE, Gearry RB, et al. Probiotic effects on intestinal fermentation patterns in patients with irritable bowel syndrome [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(32): 50205024. |
| 25. | Zeng J, Li YQ, Zuo XL, et al. Clinical trial: effect of active lactic acid bacteria on mucosal barrier function in patients with diarrhoeapredominant irritable bowel syndrome [J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2008, 28(8): 9941002. |
| 26. | Andriulli A, Neri M, Loguercio C, et al. Clinical trial on the efficacy of a new symbiotic formulation, Flortec, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a multicenter, randomized study [J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 42 Suppl 3 Pt 2: S218S223. |
| 27. | Furrie E, Macfarlane S, Kennedy A, et al. Synbiotic therapy (Bifidobacterium longum/Synergy 1) initiates resolution of inflammation in patients with active ulcerative colitis: a randomised controlled pilot trial [J]. Gut, 2005, 54(2): 242249. |
| 28. | Garcia Vilela E, De Lourdes De Abreu Ferrari M, Oswaldo Da Gama Torres H, et al. Influence of Saccharomyces boulardii on the intestinal permeability of patients with Crohn’s disease in remission [J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2008, 43(7): 842848. |
| 29. | Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an antiinflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(43): 1673116736. |
| 30. | Hedin C, Whelan K, Lindsay JO. Evidence for the use of probiotics and prebiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of clinical trials [J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2007, 66(3): 307315. |
| 31. | Francavilla R, Lionetti E, Castellaneta SP, et al. Inhibition of helicobacter pylori infection in humans by lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 and effect on eradication therapy: a pilot study [J]. Helicobacter, 2008, 13(2): 127134. |
| 32. | Saavedra J. Probiotics and infectious diarrhea [J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2000, 95(1 Suppl): S16S18. |
| 33. | Corrêa NB, Péret Filho LA, Penna FJ, et al. A randomized formula controlled trial of Bifidobacterium lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus for prevention of antibioticassociated diarrhea in infants [J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2005, 39(5): 385389. |
| 34. | Rafter J, Bennett M, Caderni G, et al. Dietary synbiotics reduce cancer risk factors in polypectomized and colon cancer patients [J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2007, 85(2): 488496. |
| 35. | Hatakka K, Holma R, ElNezami H, et al. The influence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LC705 together with Propionibacterium freudenreichii SSP. shermanii JS on potentially carcinogenic bacterial activity in human colon [J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2008, 128(2): 406410. |
| 36. | Tangney M. Gene therapy for cancer: dairy bacteria as delivery vectors [J]. Discov Med, 2010, 10(52): 195200. |
| 37. | Reddy BS, Macfie J, Gatt M, et al. Randomized clinical trial of effect of synbiotics, neomycin and mechanical bowel preparation on intestinal barrier function in patients undergoing colectomy [J]. Br J Surg, 2007, 94(5): 546554. |
| 38. | Gill HS, Rutherfurd KJ, Cross ML, et al. Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 [J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2001, 74(6): 833839. |
| 39. | Sugawara G, Nagino M, Nishio H, et al. Perioperative synbiotic treatment to prevent postoperative infectious complications in biliary cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Ann Surg, 2006, 244(5): 706714. |
| 40. | Pitsouni E, Alexiou V, Saridakis V, et al. Does the use of probiotics/synbiotics prevent postoperative infections in patients undergoing abdominal surgery? A metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2009, 65(6): 561570. |
| 41. | Liu Z, Qin H, Yang Z, et al. Randomised clinical trial: the effects of perioperative probiotic treatment on barrier function and postoperative infectious complications in colorectal cancer surgery-a doubleblind study [J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 33(1): 5063. |
| 42. | Sanders ME, Tompkins T, Heimbach JT, et al. Weight of evidence needed to substantiate a health effect for probiotics and prebiotics: regulatory considerations in Canada, E.U., and U.S [J]. Eur J Nutr, 2005, 44(5): 303310. |
| 43. | Oláh A, Belágyi T, Issekutz A, et al. Randomized clinical trial of specific lactobacillus and fibre supplement to early enteral nutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis [J]. Br J Surg, 2002, 89(9): 11031107. |
| 44. | Oláh A, Belágyi T, Pótó L, et al. Synbiotic control of inflammation and infection in severe acute pancreatitis: a prospective, randomized, double blind study [J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2007, 54(74): 590594. |
| 45. | Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Buskens E, et al. Probiotic prophylaxis in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, doubleblind, placebocontrolled trial [J]. Lancet, 2008, 371(9613): 651659. |
| 46. | McClave S, Heyland DK, Wischmeyer PE. Expression of concern-Probiotic prophylaxis in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, doubleblind, placebocontrolled trial [J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2010, 375(9718): 875876. |
| 47. | Floch MH, Walker WA, Guandalini S, et al. Recommendations for probiotic use-2008 [J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 42 Suppl 2: S104S108. |
| 48. | Rautio M, JousimiesSomer H, Kauma H, et al. Liver abscess due to a Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain indistinguishable from L. rhamnosus strain GG [J]. Clin Infect Dis, 1999, 28(5): 11591160. |
| 49. | Land MH, RousterStevens K, Woods CR, et al. Lactobacillus sepsis associated with probiotic therapy [J]. Pediatrics, 2005, 115(1): 178181. |
| 50. | Quigley EM. New perspectives on the role of the intestinal flora in health and disease [J]. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2006, 15(2): 109110. |
- 1. Sartor RB. Microbial influences in inflammatory bowel diseases [J]. Gastroenterology, 2008, 134(2): 577594.
- 2. Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, et al. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity [J]. Nature, 2006, 444(7122): 10221023.
- 3. O’Hara AM, Shanahan F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ [J]. EMBO Rep, 2006, 7(7): 688693.
- 4. Cani PD, Delzenne NM. The gut microbiome as therapeutic target [J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 130(2): 202212.
- 5. Palmer C, Bik EM, DiGiulio, et al. Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota [J]. PLoS Biol, 2007, 5(7): e177.
- 6. Agans R, Rigsbee L, Kenche H, et al. Distal gut microbiota of adolescent children is different from that of adults [J]. FEMS Microbiol Ecol, 2011, 77(2): 404412.
- 7. Lyra A, Rinttil T, Nikkil J, et al. Diarrhoeapredominant irritable bowel syndrome distinguishable by 16S rRNA gene phylotype quantification [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15(47): 59365945.
- 8. Malinen E, Rinttil T, Kajander K, et al. Analysis of the fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients and healthy controls with realtime PCR [J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2005, 100(2): 373382.
- 9. Schoepfer AM, Schaffer T, SeiboldSchmid B, et al. Antibodies to flagellin indicate reactivity to bacterial antigens in IBS patients [J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2008, 20(10): 11101118.
- 10. Seksik P, RigottierGois L, Gramet G, et al. Alterations of the dominant faecal bacterial groups in patients with Crohn’s disease of the colon [J]. Gut, 2003, 52(2): 237242.
- 11. Turner JR. Molecular basis of epithelial barrier regulation: from basic mechanisms to clinical application [J]. Am J Pathol, 2006, 169(6): 19011909.
- 12. Barnich N, Carvalho FA, Glasser AL, et al. CEACAM6 acts as a receptor for adherentinvasive E.coli, supporting ileal mucosa colonization in Crohn disease [J]. J Clin Invest, 2007, 117(6): 15661574.
- 13. de Giorgio R, Blandizzi C. Targeting enteric neuroplasticity: diet and bugs as new key factors [J]. Gastroenterology, 2010, 138(5): 16631666.
- 14. Nalini N, Manju V, Menon VP. Effect of coconut cake on the bacterial enzyme activity in 1,2dimethyl hydrazine induced colon cancer [J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2004, 342(12): 203210.
- 15. Iwashita J, Sato Y, Sugaya H, et al. mRNA of MUC2 is stimulated by IL4, IL13 or TNFα through a mitogenactivated protein kinase pathway in human colon cancer cells [J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2003, 81(4): 275282.
- 16. Shimizu K, Ogura H, Asahara T, et al. Gastrointestinal dysmotility is associated with altered gut flora and septic mortality in patients with severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome: a preliminary study [J]. Neurogastroenterol Motil, 2011, 23(4): 330335, e157.
- 17. Reddy BS, Gatt M, Sowdi R, et al. Surgical manipulation of the large intestine increases bacterial translocation in patients undergoing elective colorectal surgery [J]. Colorectal Dis, 2006, 8(7): 596600.
- 18. Li JV, Ashrafian H, Bueter M, et al. Metabolic surgery profoundly influences gut microbialhost metabolic crosstalk [J]. Gut, 2011, 60(9): 12141223.
- 19. Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins [J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7228): 480484.
- 20. Limdi JK, O’Neill C, McLaughlin J. Do probiotics have a therapeutic role in gastroenterology? [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2006, 12(34): 54475457.
- 21. Preidis GA, Versalovic J. Targeting the human microbiome with antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics: gastroenterology enters the metagenomics era [J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 136(6): 20152031.
- 22. Moayyedi P, Ford AC, Talley NJ, et al. The efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review [J]. Gut, 2010, 59(3): 325332.
- 23. Hun L. Bacillus coagulans significantly improved abdominal pain and bloating in patients with IBS [J]. Postgrad Med, 2009, 121(2): 119124.
- 24. Barrett JS, Canale KE, Gearry RB, et al. Probiotic effects on intestinal fermentation patterns in patients with irritable bowel syndrome [J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(32): 50205024.
- 25. Zeng J, Li YQ, Zuo XL, et al. Clinical trial: effect of active lactic acid bacteria on mucosal barrier function in patients with diarrhoeapredominant irritable bowel syndrome [J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2008, 28(8): 9941002.
- 26. Andriulli A, Neri M, Loguercio C, et al. Clinical trial on the efficacy of a new symbiotic formulation, Flortec, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a multicenter, randomized study [J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 42 Suppl 3 Pt 2: S218S223.
- 27. Furrie E, Macfarlane S, Kennedy A, et al. Synbiotic therapy (Bifidobacterium longum/Synergy 1) initiates resolution of inflammation in patients with active ulcerative colitis: a randomised controlled pilot trial [J]. Gut, 2005, 54(2): 242249.
- 28. Garcia Vilela E, De Lourdes De Abreu Ferrari M, Oswaldo Da Gama Torres H, et al. Influence of Saccharomyces boulardii on the intestinal permeability of patients with Crohn’s disease in remission [J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2008, 43(7): 842848.
- 29. Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an antiinflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2008, 105(43): 1673116736.
- 30. Hedin C, Whelan K, Lindsay JO. Evidence for the use of probiotics and prebiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of clinical trials [J]. Proc Nutr Soc, 2007, 66(3): 307315.
- 31. Francavilla R, Lionetti E, Castellaneta SP, et al. Inhibition of helicobacter pylori infection in humans by lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 and effect on eradication therapy: a pilot study [J]. Helicobacter, 2008, 13(2): 127134.
- 32. Saavedra J. Probiotics and infectious diarrhea [J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2000, 95(1 Suppl): S16S18.
- 33. Corrêa NB, Péret Filho LA, Penna FJ, et al. A randomized formula controlled trial of Bifidobacterium lactis and Streptococcus thermophilus for prevention of antibioticassociated diarrhea in infants [J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2005, 39(5): 385389.
- 34. Rafter J, Bennett M, Caderni G, et al. Dietary synbiotics reduce cancer risk factors in polypectomized and colon cancer patients [J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2007, 85(2): 488496.
- 35. Hatakka K, Holma R, ElNezami H, et al. The influence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus LC705 together with Propionibacterium freudenreichii SSP. shermanii JS on potentially carcinogenic bacterial activity in human colon [J]. Int J Food Microbiol, 2008, 128(2): 406410.
- 36. Tangney M. Gene therapy for cancer: dairy bacteria as delivery vectors [J]. Discov Med, 2010, 10(52): 195200.
- 37. Reddy BS, Macfie J, Gatt M, et al. Randomized clinical trial of effect of synbiotics, neomycin and mechanical bowel preparation on intestinal barrier function in patients undergoing colectomy [J]. Br J Surg, 2007, 94(5): 546554.
- 38. Gill HS, Rutherfurd KJ, Cross ML, et al. Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 [J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2001, 74(6): 833839.
- 39. Sugawara G, Nagino M, Nishio H, et al. Perioperative synbiotic treatment to prevent postoperative infectious complications in biliary cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Ann Surg, 2006, 244(5): 706714.
- 40. Pitsouni E, Alexiou V, Saridakis V, et al. Does the use of probiotics/synbiotics prevent postoperative infections in patients undergoing abdominal surgery? A metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2009, 65(6): 561570.
- 41. Liu Z, Qin H, Yang Z, et al. Randomised clinical trial: the effects of perioperative probiotic treatment on barrier function and postoperative infectious complications in colorectal cancer surgery-a doubleblind study [J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2011, 33(1): 5063.
- 42. Sanders ME, Tompkins T, Heimbach JT, et al. Weight of evidence needed to substantiate a health effect for probiotics and prebiotics: regulatory considerations in Canada, E.U., and U.S [J]. Eur J Nutr, 2005, 44(5): 303310.
- 43. Oláh A, Belágyi T, Issekutz A, et al. Randomized clinical trial of specific lactobacillus and fibre supplement to early enteral nutrition in patients with acute pancreatitis [J]. Br J Surg, 2002, 89(9): 11031107.
- 44. Oláh A, Belágyi T, Pótó L, et al. Synbiotic control of inflammation and infection in severe acute pancreatitis: a prospective, randomized, double blind study [J]. Hepatogastroenterology, 2007, 54(74): 590594.
- 45. Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Buskens E, et al. Probiotic prophylaxis in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, doubleblind, placebocontrolled trial [J]. Lancet, 2008, 371(9613): 651659.
- 46. McClave S, Heyland DK, Wischmeyer PE. Expression of concern-Probiotic prophylaxis in predicted severe acute pancreatitis: a randomised, doubleblind, placebocontrolled trial [J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2010, 375(9718): 875876.
- 47. Floch MH, Walker WA, Guandalini S, et al. Recommendations for probiotic use-2008 [J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 42 Suppl 2: S104S108.
- 48. Rautio M, JousimiesSomer H, Kauma H, et al. Liver abscess due to a Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain indistinguishable from L. rhamnosus strain GG [J]. Clin Infect Dis, 1999, 28(5): 11591160.
- 49. Land MH, RousterStevens K, Woods CR, et al. Lactobacillus sepsis associated with probiotic therapy [J]. Pediatrics, 2005, 115(1): 178181.
- 50. Quigley EM. New perspectives on the role of the intestinal flora in health and disease [J]. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis, 2006, 15(2): 109110.